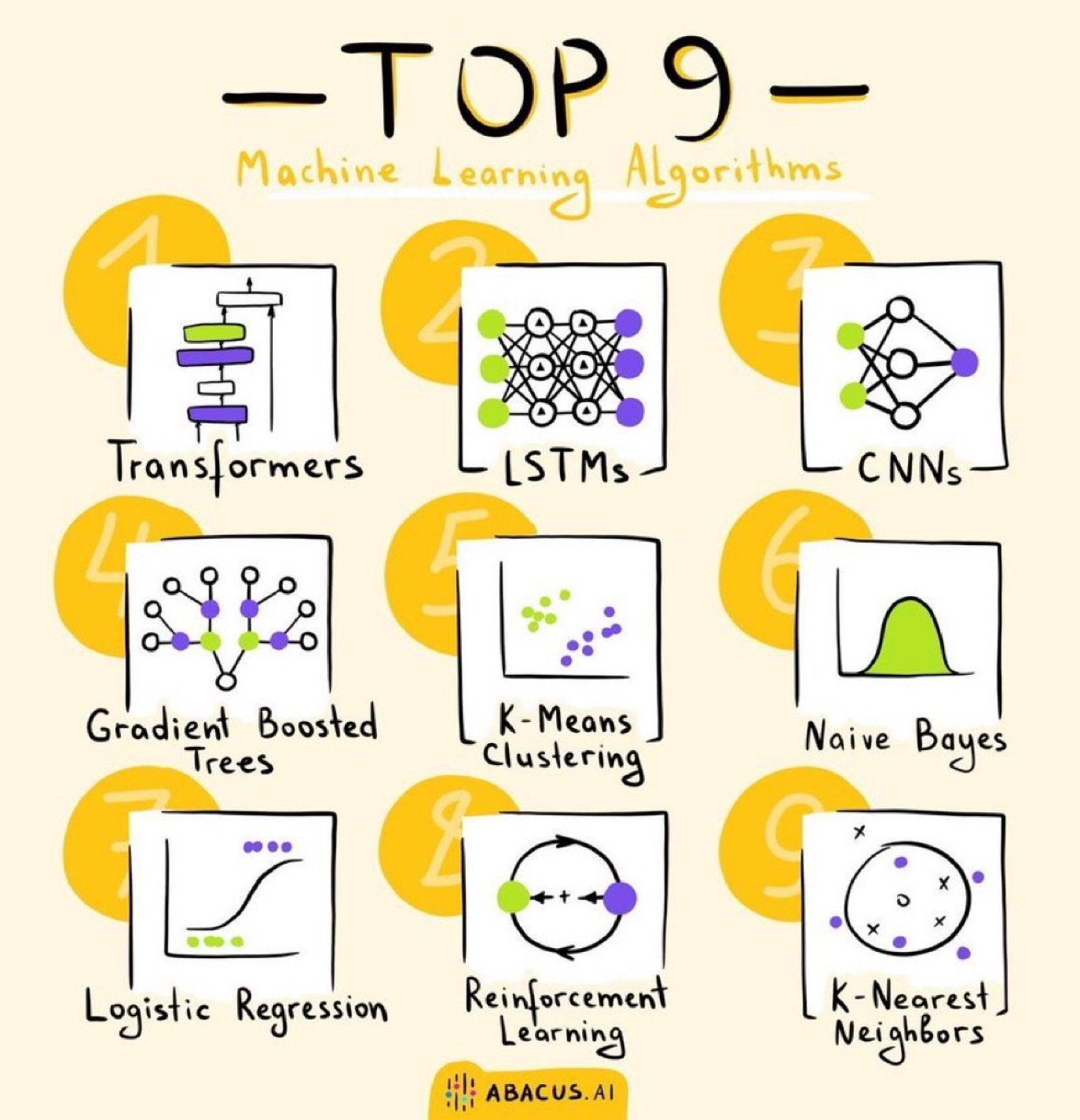
Get to know your Machine Learning Algorithms.
Transformers
Transformers led to the LLMs revolution we see today, they leverage attention mechanisms to process input data in parallel, providing swift and efficient training.
BERT and GPT are some popular architectures.
LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory):
A subtype of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), LSTMs excel at processing sequences, making them ideal for time series and language applications.
CNNs (Convolutional Neural Networks):
Predominantly used in image processing, CNNs utilize filters to scan images and identify patterns, making image classification and recognition a breeze.
Gradient Boosted Trees:
A powerful ensemble method, it builds trees sequentially, each one correcting the mistakes of its predecessor, delivering high accuracy in tasks like regression and classification.
K-means Clustering:
An unsupervised algorithm, K-means groups data into 'k' clusters by minimizing intra-cluster distances.
Naive Bayes:
A family of simple probabilistic classifiers based on applying Bayes' theorem with strong independence assumptions between the features.
Logistic Regression:
Simple yet so effective & interpretable, a lot of ML problems in the industry are still solved using linear regression. The hello world of ML.
Reinforcement Learning:
Learning to take actions in an environment in order to maximize the cumulative reward.
RLHF is used in models like ChatGPT to optimise them for human dialogue.
KNN (K-Nearest Neighbors):
A simple, intuitive method, KNN classifies an item based on how its neighbors are classified.
Like deducing a person's favorite music based on their friends' preferences.